Dealing with Browser Hijackers: Prevention Tips

Browser Hijacker: Depth Analysis
Browser hijacking is like someone sneaking into your web browser without asking and making changes you didn’t want. They might change your homepage, the page you see when you open your browser, or your search engine, where you look for stuff online.
The tricky part is that they do this to make money. Browser hijacker forces your browser to show you ads or take you to certain websites, and every time you click on those ads or pages, the app creators earn money. So, they’re making a profit by bothering you.
But it gets worse. Some of these hijackers can spy on you. They might secretly install a program that watches everything you do online, like what you type and where you go. This is really bad because they can steal your sensitive information, like your bank details or email passwords.
Sometimes, they can even mess up your computer so badly that it’s really hard to fix. While some browser hijacks are easy to undo, others can be a big headache.
So, the key is to be careful online and make sure your browser settings stay the way you want them. If you ever notice strange changes, it’s important to fix them as soon as possible to keep your online experience safe and enjoyable.
Attributes of Browser hijackers:

A browser hijacker is like an unwanted guest in your web browser that messes with your settings and can make your online experience frustrating. Here are some common things they do:
- Change Your Homepage: Browser hijackers can change the first website (homepage) you see when you open your browser.
- Switch Your Search Engine: They might change where you search for things online.
- Mess with Your Bookmarks: They can add or remove bookmarks.
- Add Extra Stuff: Some hijackers bring along unwanted toolbars, like adding more buttons to your browser that you didn’t ask for.
- Show Annoying Ads: These apps constantly pop up ads while you’re trying to surf the web.
- Send You to Weird Places: They might suddenly take you to strange websites you didn’t intend to visit.
- Block Access: They prevent you from going where you want online.
- Slow Things Down: Hijackers can make your browser sluggish and frustrating to use.
Now, here’s the tricky part: They also spy on you. They use tracking cookies to see what websites you visit and what you search for online. Then, they use this information to show you ads that they think you might click on.
So, when you see a pop-up asking about cookies on websites, it’s a bit like the hijacker asking for permission to watch what you do. Hijackers use this information to make money from ads and promotions.
Who is Behind Browser-Hijacking? Their Motives

The individuals or groups behind browser hijacking are often cybercriminals seeking to profit in various ways. Their motives typically revolve around financial gain and may include the following:
- Ad Revenue: Many hijacking apps are driven by the desire to make money through online advertising. By forcefully redirecting users to specific websites or displaying intrusive ads, hijackers generate income through pay-per-click advertising or affiliate marketing programs. They get paid when users click on the ads or engage with promoted content.
- Data Collection: Some hijackers aim to collect valuable user data, such as browsing habits, search queries, and personal information. They gather this data covertly and then sell it to third-party advertisers or marketers, who use it for targeted advertising, identity theft, or other malicious purposes.
- Distributing Malware: Browser-based infections can serve as a gateway for the distribution of malware, including viruses, spyware, or ransomware. They may exploit vulnerabilities in a user’s system or trick them into downloading malicious software, leading to further cyber-attacks.
- Affiliate Fraud: In some cases, browser hijackers engage in affiliate fraud by generating illegitimate clicks or impressions on advertising links. This fraudulent activity boosts the hijacker’s earnings while draining the budgets of advertisers.
- Promoting Fake Products or Services: Some hijackers are part of larger schemes to promote fake or low-quality products and services. They deceive users into making purchases, often for non-existent or subpar items, which results in financial losses for victims.
In summary, those behind browser hijacking are motivated by financial gain, data exploitation, and various deceptive practices. Their actions can harm users by compromising online security, invading privacy, and promoting scams.
Types of Browser-Hijacker

Browser hijackers come in various forms, each with its own characteristic and impact on a user’s browsing experience. Here are some common types of browser hijackers:
- Homepage Hijackers: These hijackers change your browser’s homepage to a different website without your consent. When you open your browser, you’re taken to a webpage you didn’t choose.
- Search Engine Hijackers: Search engine hijackers alter your default search engine to one of their choosing. When you perform a search in your browser’s address bar, it takes you to a search engine you didn’t pick.
- New Tab Page Hijackers: Instead of opening a blank page when you open a new tab, these hijackers force your browser to display a specific website or search engine.
- Toolbar Hijackers: Some browser hijackers install additional toolbars or extensions in your browser. These toolbars often come with extra buttons and features you didn’t want or need.
- Popup Hijackers: Popup hijackers generate a barrage of pop-up ads when you visit websites. These pop-ups can be annoying and may lead to unsafe websites.
- Browser Setting Hijackers: Some hijackers change various browser settings, such as security and privacy options, without your knowledge.
- Browser Extension or Add-on Hijackers: These hijackers install malicious browser extensions or add-ons that may steal your data, show unwanted ads, or redirect your browsing.
Each type of browser hijacker interferes with your online experience in its unique way, typically with the intention of generating revenue for the developers or promoting specific content.
Symptoms and Common Sign of Browser-Hijacker on the Affected Browser

Here are some common symptoms and signs that your browser may be affected by a hijacker:
- Changed Homepage: Your browser’s homepage is suddenly different, and you didn’t set it that way. It might redirect you to a suspicious search engine or a fake website.
- Altered Search Engine: The default search has been changed to something unfamiliar, and you can’t change it back.
- Suspicious Search Results: When you perform a search, you get results that seem unrelated or filled with advertisements.
- New Toolbar or Extensions: you notice new browser toolbars, extensions, or add-ons that you didn’t install, and they are difficult to remove.
- Increased Ads: You start seeing more ads than usual, including pop-ups and banners, on websites where you didn’t see them before.
- Redirects: You get redirected to unrelated websites, especially when you try to visit a specific site or search for something online.
- Sluggish Performance: Your browser becomes slower and less responsive than usual.
- Unwanted Pages on Startup: When you open your browser, it starts with multiple tabs or pages you didn’t set as your startup pages.
- Changed Settings: Your browser’s settings, such as security or privacy settings are modified without your permission.
- Inability to Change Settings: You try to change your browser settings, but they revert to the hijacker’s settings each time you restart your browser.
- Random Error Messages: You receive error messages related to websites or security issues that you haven’t encountered before.
- Unfamiliar Toolbars and Buttons: New buttons, icons, or toolbars appear on your browser that you didn’t add.
If you notice these symptoms on your web browser, it’s likely that your browser has been hijacked.
Potential Security Risk Caused by Browser-Hijacker

Browser hijackers might not sound as scary as other computer threats, but they can lead to some big problems. Here’s what can happen:
They can change where your browser takes you. Instead of going to safe websites, they can make you go to bad places on the internet, some of which have nasty computer viruses. Besides, you know those annoying ads that pop up when you’re online? Hijackers can use them to trick you into clicking on things. Sometimes, even the “X” or “Close” buttons on these ads can secretly install more bad stuff on your computer.
Sometimes, you don’t even have to click on anything. Hijackers can quietly download bad stuff to your computer without you knowing, just by visiting a certain website. Additionally, some hijackers are like spies. They watch what you do online and can even steal your private info, like your passwords and bank details. With your personal info, hijackers can pretend to be you and do bad things, like stealing your money or tricking others in your name. It’s like someone wearing a mask with your face.
In the worst cases, browser-based threats can bring ransomware in your device that completely controls your PC. They can lock your files, steal more info, or use your computer to attack others. So, even though browser hijackers might not be the biggest villains on the internet, they can open the door to a lot of trouble. That’s why it’s important to be careful online, avoid shady websites, and make sure you have strong security to keep these sneaky intruders out.
Exploring the Browser-Hijacker Risk

Once a browser hijacker invades your PC, it may lead to various severe issues. Let’s take a closer look at the risk associated with such an app:
The changes made by hijackers on the affected browsers are often frustrating and can disrupt your browsing experience. Moreover, one of the primary risks of browser hijackers is their ability to redirect you to malicious websites. These sites may host malware, phishing pages, or fraudulent content. You might think you’re visiting a legitimate site, but the hijacker can take you to a dangerous place.
Furthermore, browser-based infections can expose you to various forms of malware, including viruses, Trojans, and ransomware. When you’re rerouted to malevolent sites, you may unknowingly download harmful software onto your device, putting your data and privacy at risk. These apps often generate intrusive pop-up ads. Some of these ads can mimic system alerts, such as virus warnings, which may lead you to download fake antivirus software or disclose personal information to cybercriminals.
As mentioned earlier, hijackers may contain spyware components that monitor your online activity. They can capture your sensitive information like login credentials, credit card numbers, and personal messages. This data can be used for identity theft or sold on the dark web. Furthermore, they can slow down your browser, making it less responsive. Constant redirects, pop-ups, and unwanted changes can disrupt your work or leisure activities.
Bear in mind that if a browser hijacker gains access to your personal and financial data, it can lead to financial loss and other serious consequences, such as credit card fraud or unauthorized access to your accounts. Also, they often serve as a gateway for other malware. By clicking on deceptive ads or links presented by the hijacker, you may inadvertently download additional malicious software onto your device. Another thing about these parasites is that removing them can be challenging. They may hide within your system files or reinstall themselves even after you’ve removed them. This persistence makes them particularly frustrating to deal with.
In short, while browser hijackers may not be as devastating as some other forms of malware, they pose significant risks to your online security, privacy, and overall digital experience.
Real Life Instance of Browser Hijacker Exploitation
Recent cyberattacks have caused significant problems and affected large organizations. Here’s what happened:
- Hot Topic Attacks: In August 2023, the popular retailer Hot Topic faced a cyberattack. Bad actors tried to get into customer accounts on their website and mobile app using stolen login details (like email addresses and passwords). These attackers got these credentials from somewhere else, not directly from Hot Topic.
- Finnish Parliament Attack: In August 2022, during a session of the Finnish parliament, their website was hit by a DDoS attack. This kind of attack is like a digital traffic jam that makes a website slow or completely unavailable. It might have been part of a plan by hackers linked to Russia to disrupt the Finnish government’s online services because Finland was thinking about joining NATO.
- Facebook Cyberattack: In April 2021, a massive cyberattack hit Facebook (now called Meta). The personal information of over 530 million Facebook users, including their names, birthdays, and relationship status, was exposed online. The bad actors got this data by scraping it from Facebook in 2019. Scraping is like taking information from a public source without permission.
These attacks show how cybercriminals are using advanced methods to target big organizations and steal sensitive data.
What are the Methods for Browser Hijacker Infiltration?
Browser hijackers often sneak onto your computer without you realizing it. They can come in tricky forms like toolbars or sneaky browser extensions that quietly watch what you do online and sell your data.
But that’s not the only way they get in. Sometimes, you might click on something, like a link in a tricky email, and that’s all it takes for them to sneak into your browser. Cybercriminals are experts at getting you to click on bad stuff.
Downloading from sketchy websites, especially illegal ones, is another way these hijackers can infect your device. They hang out in the dark corners of the internet, waiting for unsuspecting people to download something, and then they hitch a ride into your browser.
Even regular, legit websites can be turned into traps. Hackers can infect these websites with hijacker bugs, putting everyone who visits them in danger.
Some browser hijackers can be hidden in free or trial software (freeware or shareware) you download. They sneak in when you install these programs. So, be careful when getting free stuff online and check what you’re installing to avoid unwanted browser hijackers.
How to Remove Browser Hijacker Manually from Different Browser
We’ll look on your computer to see if there are any strange or bad programs. Sometimes, things like adware or browser hijackers can be removed manually by clicking “Uninstall” in the computer settings.
Remove browser hijacker from Chrome

Google Chrome is a very popular web browser, used by many people. Because of its popularity, some sneaky software developers create things called browser hijackers that target Chrome. These hijackers can do different things to your browser.
Sometimes, they change your start page and search engine to something you didn’t choose. This can be annoying but not too hard to fix.
But some hijackers are more troublesome. They mess up your browser in many ways. They add extensions you didn’t want, put cookies on your computer, and even change your shortcuts to go to weird websites.
When this happens, you need to reset Google Chrome. It’s like giving your browser a fresh start. This way, you can get rid of all the unwanted stuff and make Chrome work like it should again.
To reset Google Chrome, you can follow various methods, but the most effective one is outlined below for your convenience:
Method 1. Utilize the “Reset Settings” option to restore Chrome to its default state
To do this, follow these steps:
- Open Chrome and click the three vertical dots in the top-right corner.
- Select “Settings.”
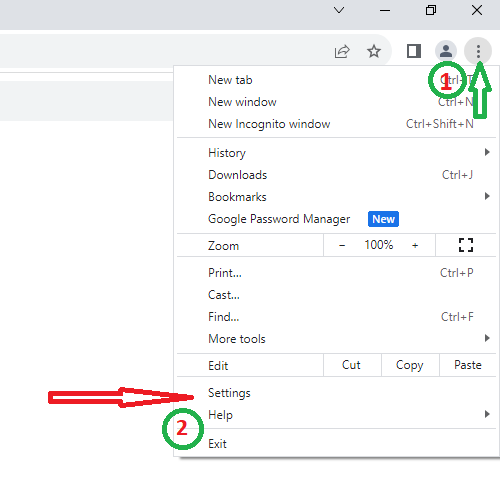
- Find “Reset Settings” and click it.
- A table will pop up, click “Reset settings” to confirm.

- Close and reopen Chrome.
This process will clear any changes or problems caused by unwanted extensions or settings. It’s like giving Chrome a fresh start, making it work smoothly again.
Method 2. Easily reach the Chrome reset page for a quick reset
In Method 1, we showed you how to reset Chrome in six steps. But there’s a faster way. Just copy and paste “chrome://settings/resetProfileSettings” into your browser’s address bar, then press Enter. This will take you straight to the Chrome reset page, and you can start the reset right away. It’s a shortcut to get things done quickly.

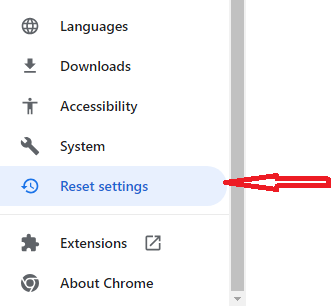
Method 3. Reset Chrome using the Flags panel for quick resetting
You can also reset Chrome by going into the “Flags” control panel, which is a bit like the method we talked about in step 2. Instead of using a quick link, type “Chrome://flags” into the address bar and press enter. A new window will pop up, and there, you can choose “Reset all.”
However, keep in mind that this method is a bit experimental. It might work to fix some problems caused by unwanted changes, but it might not work for everything. So, use it cautiously and understand that there’s a little risk involved when using this method.
Method 4. Reset Google Chrome: Delete Default User profile for a fresh start
To reset Google Chrome, follow these steps:
- Click “Start” and type “run” in the search bar, then press Enter to open the “Run” window.
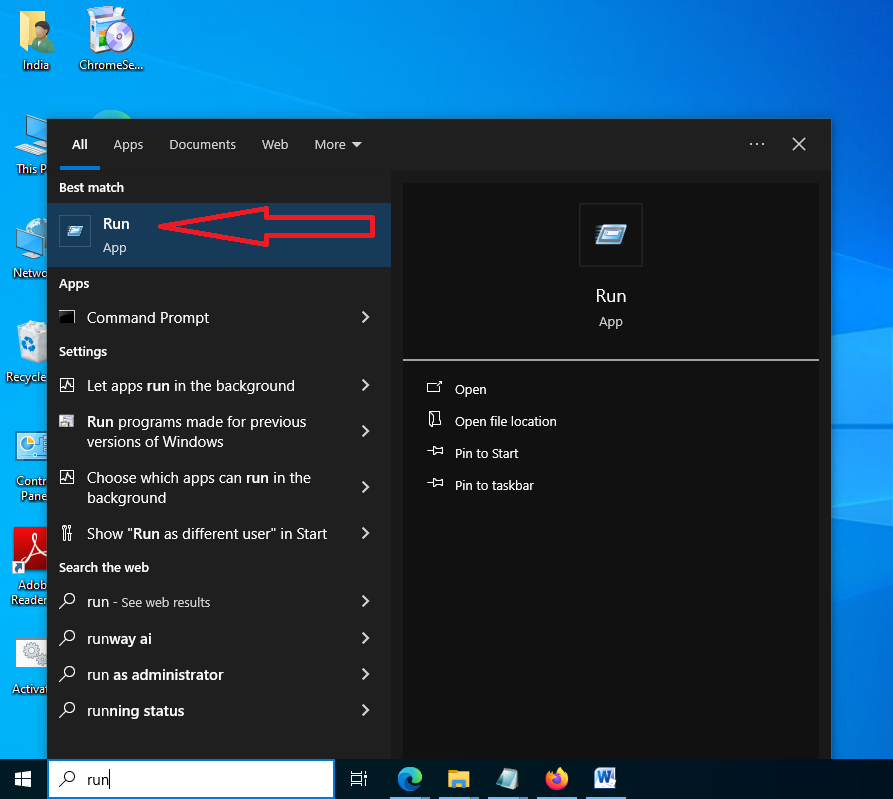
- In the “Run” window, type “%appdata%” and click “OK.” This will take you to the “Roaming” folder.

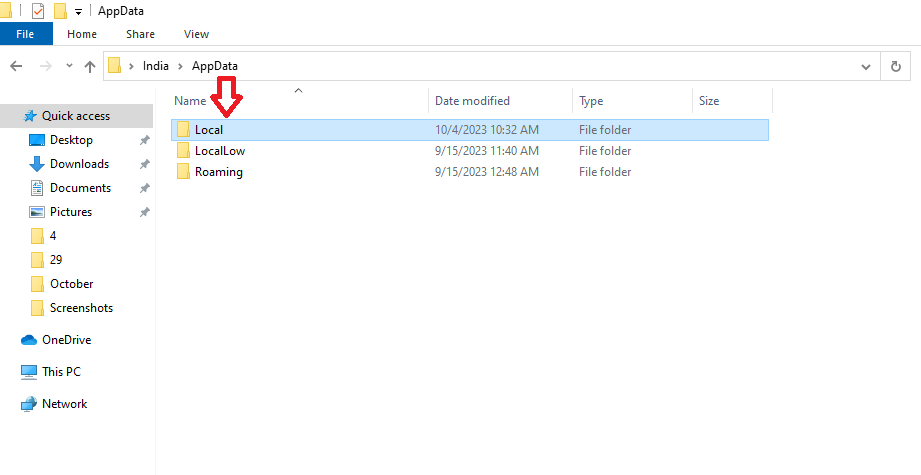
- Inside the “Roaming” folder, go up one level to the “AppData” folder.

- Navigate to “Local” -> “Google” -> “Chrome” -> “User Data.” The full path is usually something like C:\Users\YourUsername\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data, with “YourUsername” being your computer’s username.
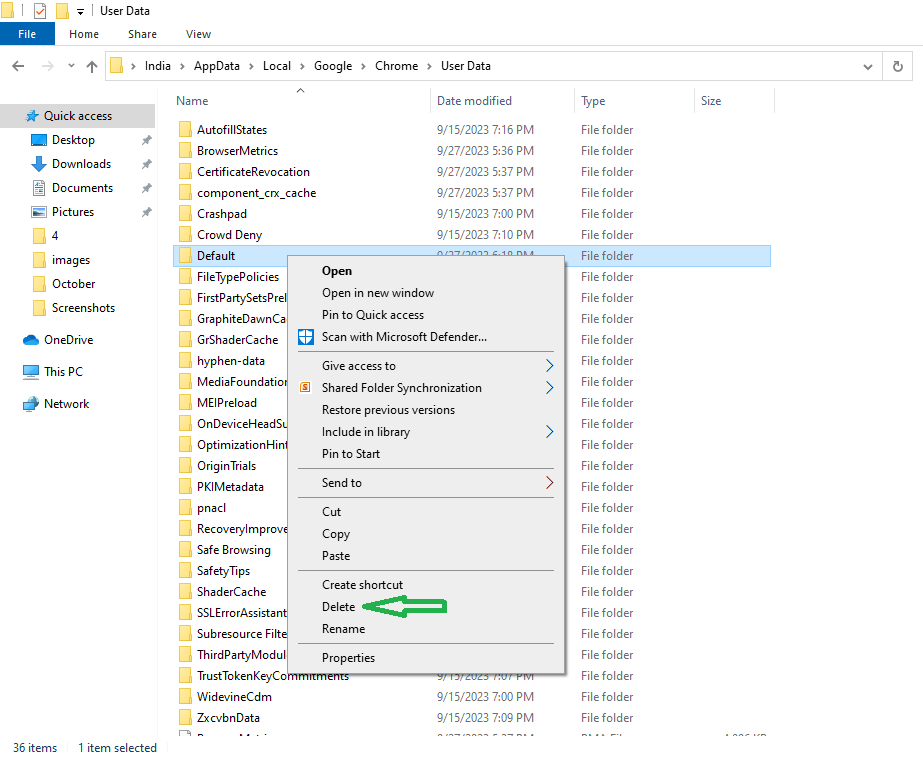
- Inside the “User Data” folder, you’ll see a folder called “Default.” Before doing anything, make a backup of this folder.
- Right-click on the “Default” folder and exit Chrome if it’s running.

- Finally, delete the “Default” folder. This action will remove your Chrome user data, including bookmarks, history, cookies, and cache, resetting Chrome to its default settings.
Method 5. Reinstall Google Chrome browser
If other fixes haven’t worked and your Chrome is still causing problems, the last resort is to reinstall it. Before you do that, make sure to completely remove all parts of the current Chrome.
To remove Google Chrome from Windows 10:
- Close all Chrome windows and tabs.
- Click the “Settings” icon in the Start menu (it looks like a gear wheel).
- Go to “Apps.”
- Find Google Chrome in the list.
- Select it.
- Click “Uninstall.”

- Confirm by clicking “Uninstall.”
- If you want to remove your browsing data, check “Also delete your browsing data.”
- Finally, click “Uninstall.” This will remove Chrome from your computer and, if you chose, delete your browsing data as well.
To uninstall Google Chrome on Windows 8 and Vista:
- Close all Chrome windows.
- Go to the “Control Panel.”

- Choose “Uninstall a program” or “Programs and Features.”
- Find Google Chrome.
- Check the box that says “Also delete your browsing data.”
- Click “Uninstall.” This will remove Chrome and, if you want, delete your browsing data.
Once you’ve removed Chrome, visit the official Google Chrome website to download and install it again. Be careful and only download it from the official site. Avoid unknown third-party websites because they might offer harmful versions bundled with bad stuff that can harm your computer. Stick to the official source to keep your PC safe.
Remove browser hijacker from Firefox
Firefox is a popular web browser, but it’s not immune to problems. Some sneaky software can hijack it and make it do things you don’t want. These hijackers can change your browser settings, like your homepage and search engine, and force you to visit unwanted websites.
Sometimes, hijackers can make small changes that regular users might not notice, like messing with your DNS settings, search results, tracking cookies, or adding extensions you didn’t ask for.
Firefox tries to protect you from bad stuff with built-in security features, but it’s not perfect. If a hijacker gets through, you need to do two things to fix it:
First, you have to get rid of the hijacker from your computer. This often means using good antivirus software.
Second, you need to remove any bad extensions the hijacker added to Firefox. You can do this by resetting Firefox to its default settings.
Resetting Mozilla Firefox clears added extensions, themes, and certain settings, but it leaves your bookmarks, browsing history, and cookies untouched. This process removes website permissions, extra search engines, download data, and various customizations. However, it doesn’t touch your open tabs, personal dictionary, or auto-fill info. It’s like giving your browser a fresh start while keeping your important stuff safe.
For resetting Mozilla Firefox, you can use different methods, but here’re some effective ones for your ease:
Method 1. Reset Firefox via Troubleshooting Information
To reset Firefox:
- Open Firefox and click the three-bar button.
- Now select “Help”
- Select “Troubleshooting Information.”
- Click “Refresh Firefox” and confirm.
- When the “Import Wizard” appears, click “Finish.” This will reset Firefox to its default settings, resolving issues.
Method 2. Easily reach Mozilla’s reset page
To quickly reset Mozilla Firefox:
- Open Firefox and type “about:support” in the address bar, then press Enter.

- On the right, find “Give Firefox a tune-up” and click “Refresh Firefox.”
- Confirm by clicking “Refresh Firefox” in the pop-up.
- Firefox will close and restart. An “Import Wizard” will show items added after the reset. Just click “Finish.”
Method 3. Reset Firefox without launching it
To reset Firefox without opening it normally:
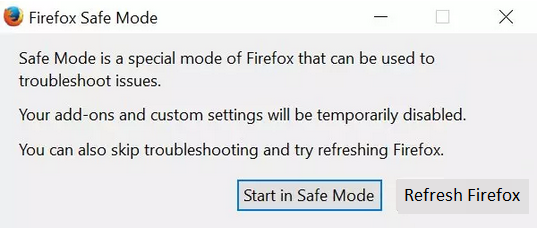
- Open Firefox in “Safe Mode” by holding the Shift key while trying to launch it. If that doesn’t work, use your computer’s search to find the “Mozilla Firefox (Safe Mode)” shortcut.

- If you have multiple user profiles, you’ll be asked to choose one. Hold Shift while selecting the profile. If you have only one profile, you’ll see a message about Firefox Safe Mode.
- Click “Refresh Firefox” in Safe Mode to start the reset process.
Method 4. Reset Firefox via Profile Manager
To reset Firefox using the Profile Manager:
- Press Windows key + R to open the Run prompt.
- Type “firefox.exe -p” or “firefox.exe -P” and press OK.
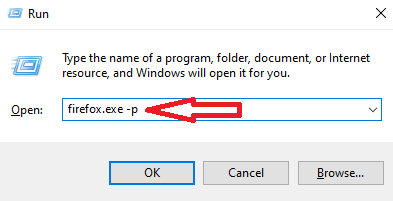
- In the Firefox Profile Manager, select “default” and click “Delete Profile.”

- Confirm by clicking “Delete Files.”

- Finally, click “Exit.” This process resets Firefox by removing the profile, which includes your settings and data.

When you reopen Firefox, the Import Wizard appears. It asks where you want to import settings, bookmarks, passwords, history, and more from, helping you set up your browser again.
Method 5. Reinstall Mozilla Firefox browser
If your Firefox browser still has issues after trying these fixes, you can reinstall it. This means you remove it and then download it again. Here’s how:
- Close Firefox: Click the three horizontal lines in the upper-right corner of Firefox (the menu button) and select “Exit” to close the browser.
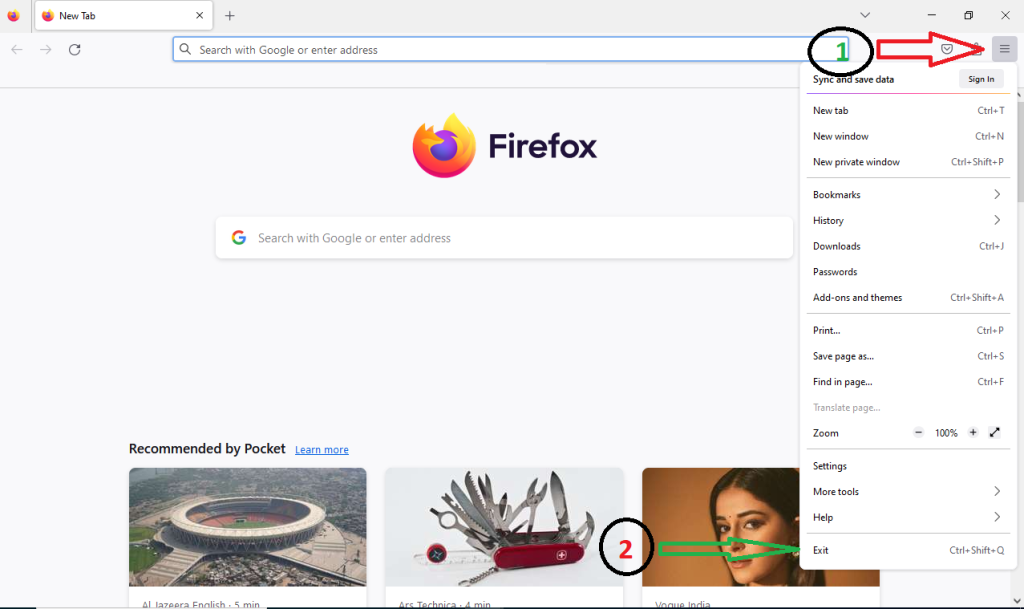
- Uninstall Firefox: Right-click on the “Start” menu (or go to “Control Panel” on Windows 7/Vista, or “Add/Remove Programs” on Windows XP). Look for “Mozilla Firefox” in the list of installed programs and click “Uninstall.”

- Use Uninstall Wizard: If the Uninstall Wizard doesn’t start, locate the “helper.exe” file in one of these folders: C:\Program Files\Mozilla Firefox\uninstall\helper.exe or C:\Program Files (x86)\Mozilla Firefox\uninstall\helper.exe. Double-click it, and when the “User Account Control” window appears, click “Yes” to continue. Follow the prompts in the Uninstall Wizard, click “Next,” “Uninstall,” and finally, “Finish.”

- Delete Firefox Folder: After uninstalling Firefox, you’ll need to delete the Firefox installation folder. Look for it in one of these locations: C:\Program Files\Mozilla Firefox or C:\Program Files (x86)\Mozilla Firefox.

- Remove User Data (Optional): If you want to remove your bookmarks, history, and other user data, press the Windows key + R on your keyboard, type “%APPDATA%\Mozilla\” and hit “OK.” In the “Mozilla” folder, you’ll see a folder named “Firefox” – delete it.
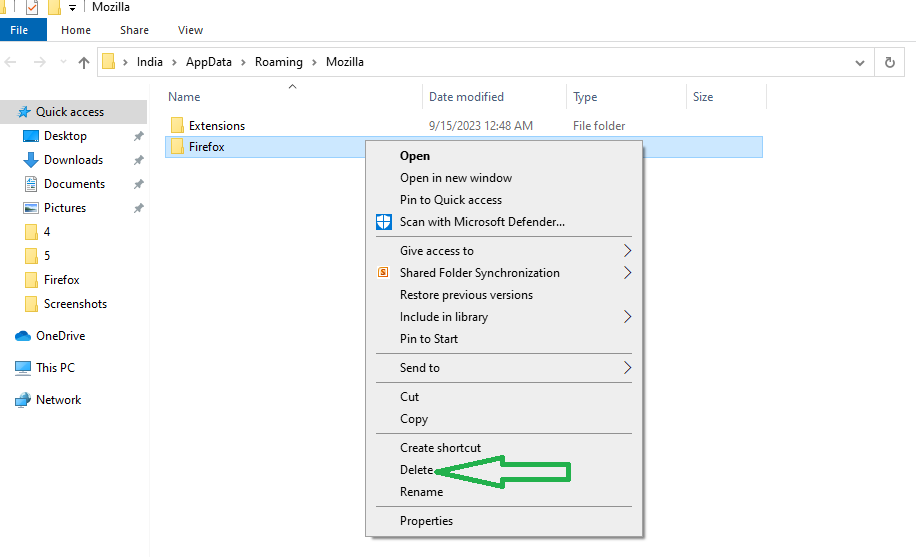
- Reinstall Firefox: Once you’ve uninstalled Firefox and removed user data (if desired), you can reinstall it. To ensure you get the safe and official version, use another browser to visit Mozilla’s official download page. Download the Firefox installer to your PC.
Remove browser hijacker from MS Edge
Microsoft Edge is a web browser that came out in 2015 with Windows 10. It’s known for being secure, but it can still get hijacked by unwanted extensions, especially if you install free software.
So, if you notice that your Edge browser isn’t acting right, like your homepage or search engine has changed without your permission, you’ll need to use a good security program to scan your computer for any nasty stuff that might have snuck in. This will help remove the bad things causing the problem.
But here’s the catch: even after you remove the bad stuff, your browser might still not be back to normal. You’ll have to manually reset it to its default settings. Don’t worry; it’s not too complicated. You can follow the instructions for resetting Microsoft Edge to make it work properly again.
There are multiple methods to reset Microsoft Edge. We offer four solutions, and the choice depends on the severity of the issue. For minor problems, quicker fixes may work. However, if you’re dealing with a potentially unwanted program, it’s best to perform a complete reset. Let’s continue with the step-by-step instructions.
Method 1. Clear Edge data to reset the browser
To reset Microsoft Edge by clearing browser data, follow these steps:
- Open Microsoft Edge and click on the three-dot icon in the upper-right corner (that’s the menu button). Then, scroll down and click on “Settings.”
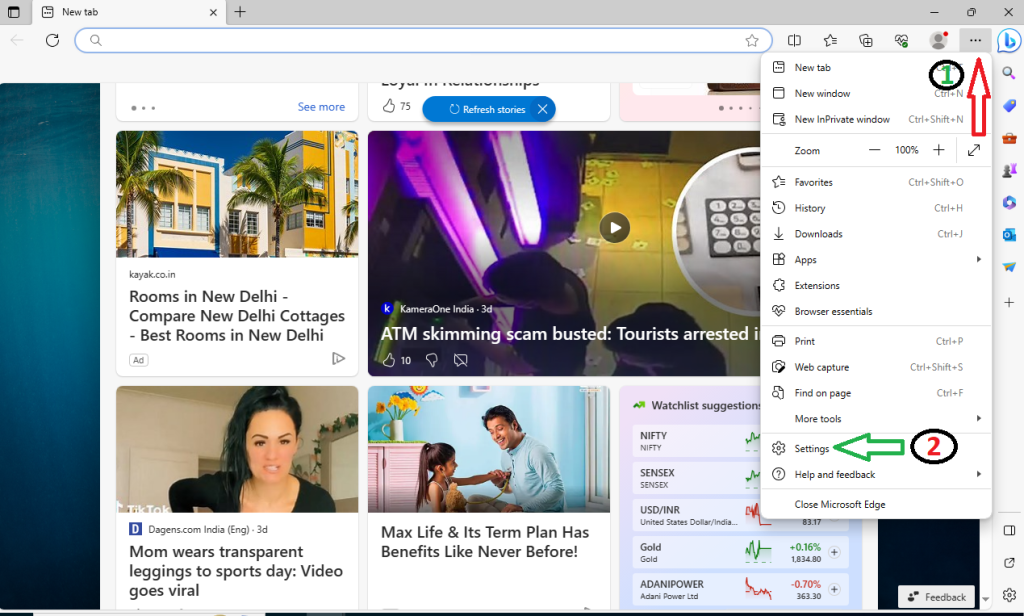
- Look for or search in the search box “Clear Browsing Data” option and click on “Choose what to clear.”
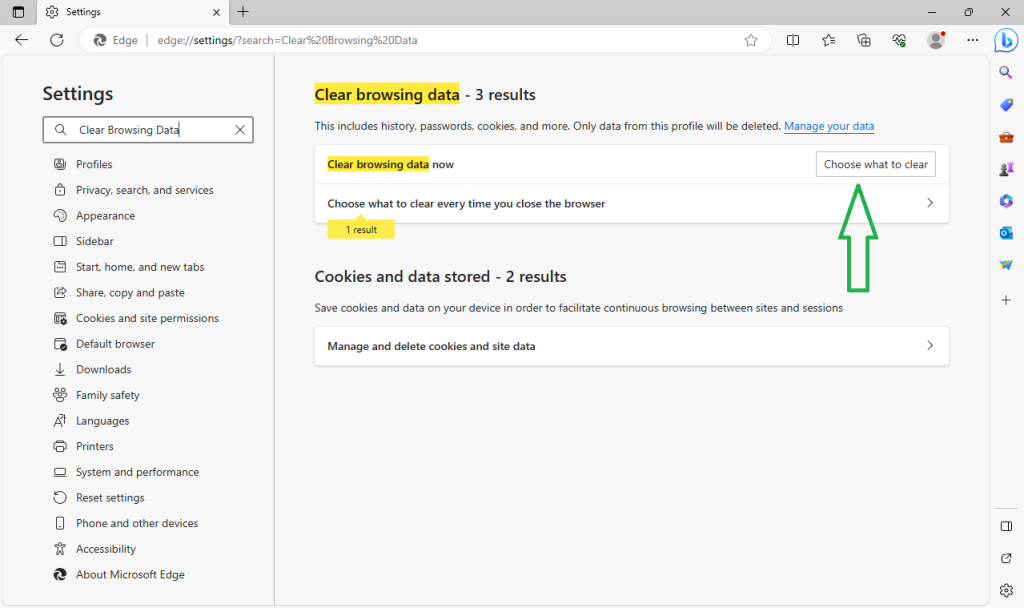
- A new window will pop up, showing different types of data. Usually, the first three or four options are automatically selected, but it’s a good idea to check all. Then, click the “Clear Now” button.
If your Microsoft Edge is not responding and you can’t start the reset because the browser won’t close, here’s what you can do:
- Click the “Start” button and open “Task Manager.”

- In the list of processes, find “Microsoft Edge.” Right-click on each entry and choose “Go to details.”

- In the details tab, find the Microsoft Edge entries again, right-click on them, and select “End Task.”
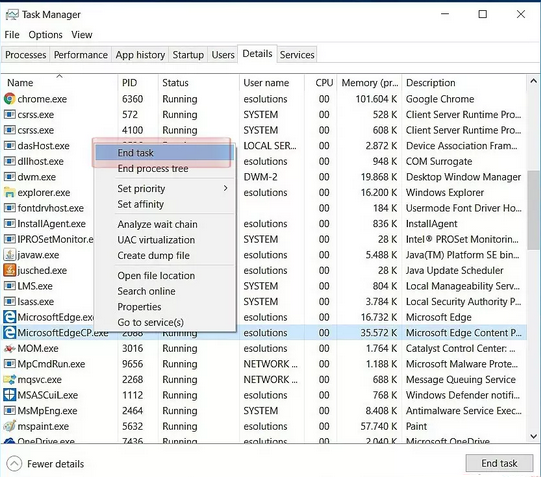
This will help you force-close Microsoft Edge so you can proceed with the reset. Remember, clearing your browser data can help fix issues and make your browser work smoothly again.
Method 2. Utilize PowerShell to perform a Microsoft Edge reset
If Microsoft Edge is giving you trouble, like running slow, not loading websites, or showing error messages, you can try this method to fix it:
- Create a new administrator account on your computer. You can do this by opening “File Explorer” and typing in the following: C:\Users\%username%\AppData\Local\Packages\Microsoft.MicrosoftEdge_8wekyb3d8bbwe

- Select the existing folders, right-click on them, and choose “Delete.”

- Go back to your regular account and open “PowerShell.” You can do this by pressing the Windows button or clicking the Start icon, then typing “powershell.” Right-click on it and select “Run as administrator.”
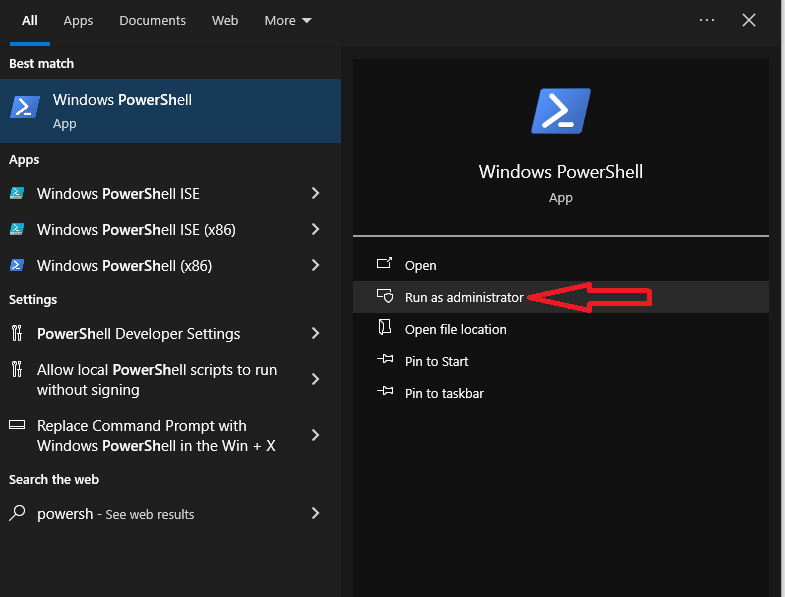
- In the PowerShell window, paste this command: Get-AppXPackage -AllUsers -Name Microsoft.MicrosoftEdge | Foreach {Add-AppxPackage -DisableDevelopmentMode -Register “$($_.InstallLocation)\AppXManifest.xml” -Verbose}

- Press “Enter” and let the command run. It will reset Microsoft Edge. You’ll see the command running.
- Once it’s done, Edge will be fully reset and should work better.
- Finally, enter this command: Get-AppXPackage -AllUsers -Name Microsoft.MicrosoftEdge | Foreach {Add-AppxPackage -DisableDevelopmentMode -Register “$($_.InstallLocation)\AppXManifest.xml”}
- This will reinstall Microsoft Edge on your computer.
Method 3. Remove Microsoft Edge registry entries to eliminate user settings and preferences
If you have a problem with Microsoft Edge due to a browser hijacker or adware, you can fix it by deleting certain settings in the Windows Registry. Here’s how:
- Open the Registry Editor by pressing the Windows key and the “R” key at the same time. In the dialog box that appears, type “regedit” and press Enter.

- In the Registry Editor, go to this location: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Classes\Local Settings\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\AppContainer\Storage\microsoft.microsoftedge_8wekyb3d8bbwe\MicrosoftEdge
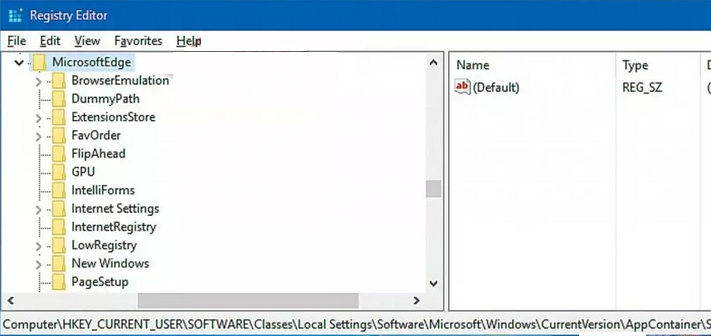
- Delete the content inside this location.
- Close the Registry Editor.
- You might see a prompt asking you to restart your device. If you do, go ahead and restart it.
Method 4. Use System File Checker to check for viruses and ensure your system is free from them
If Microsoft Edge is still not working well and you suspect something worse might be going on, you can use Command Prompt to check for hidden problems. Here’s how:
- Click the “Start” button, type “Command Prompt,” and choose “Run as administrator.”
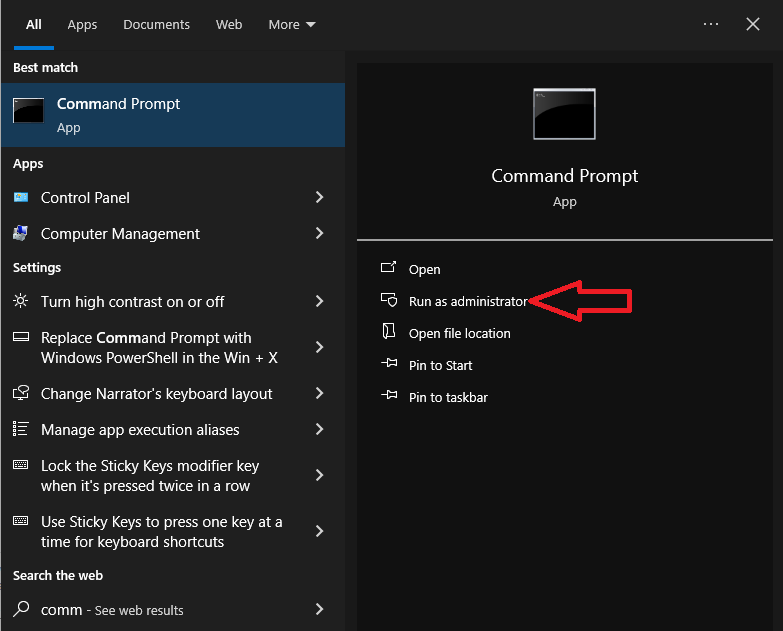
- In the Command Prompt window, type “sfc /scannow” and press Enter.
- The process will take a bit of time.

- Wait for it to finish, and it might help fix any more serious issues with Microsoft Edge.
Method 5. Reinstall Microsoft Edge
If the previous methods didn’t work, you can completely reset Microsoft Edge by uninstalling it from your computer and then downloading it again from the official website. It’s a quick process that might solve persistent problems.
Remove browser hijacker from Internet Explorer

Internet Explorer (IE) is an old web browser, and most people have moved on to newer ones like Chrome, Firefox, or Edge because IE is not very safe. But some folks still use it for old websites that were made a long time ago.
Now, if your IE gets hijacked, meaning it starts acting weird because of malware or bad stuff, you should do a few things. First, remove the bad stuff from your browser. You can use good antivirus software to help with this.
But here’s a better idea: switch to a newer Windows operating system and use a safer web browser like Chrome, Firefox, or Edge. These are more secure and better for today’s internet.
If you want to stick with IE and just need to fix it, you can reset it. This means taking it back to its original settings. Here are five ways to do it:
Method 1. Use “System File Checker” to reset Internet Explorer settings safely
Here’s how to reset Internet Explorer using the “System File Checker” option:
- If you have Windows 10, you can open Command Prompt (Admin) in two ways: by pressing Win+X and selecting it from the menu, or by typing “cmd” in the search bar, right-clicking Command Prompt, and choosing “Run as Administrator.”
- For Windows 8/8.1, go to Apps screen -> Windows System -> Command Prompt. For Windows 7, Vista, or XP, click Start -> All Programs -> Accessories -> Command Prompt.
- When a window asks for permission (User Account Control), click “Yes” to let it make changes.
- In the command line, type “SFC /SCANNOW” and press Enter.
- Wait for the process to finish. It will check for and fix any issues, including problems with Internet Explorer.
This helps ensure Internet Explorer works better by correcting any errors it might have.
Method 2. Use “Reset Settings” option to restore Internet Explorer to default
To reset Internet Explorer, follow these steps:
- Open Internet Explorer and pick “Tools” menu in the top right corner. If you don’t see the “Tools” menu, press “Alt.”

- Click on “Tools” and select “Internet Options.”
- Go to the “Advanced” tab.
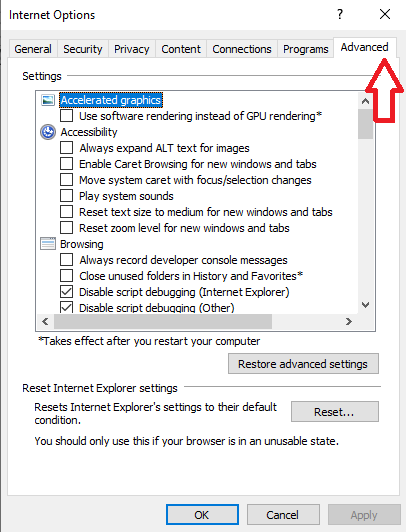
- In the “Advanced” tab, click on “Reset.” If you have an older version of IE like Internet Explorer 6, click “Restore Default.”

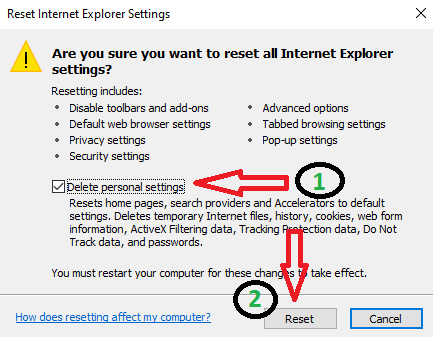
- Check the box that says “Delete personal settings” in the Reset Internet Explorer Settings box. Then, click “Reset.”

Note that this will remove your browsing history, search providers, home pages, and more.
- After Internet Explorer finishes applying the default settings, click “Close,” and then choose “OK.”
- Restart Internet Explorer, and it should be reset to its default settings.
Method 3. Reset IE via “inetcpl.cpl” command for a fresh browser start
To reset Internet Explorer:
- Close IE.
- Click Start, then Run.
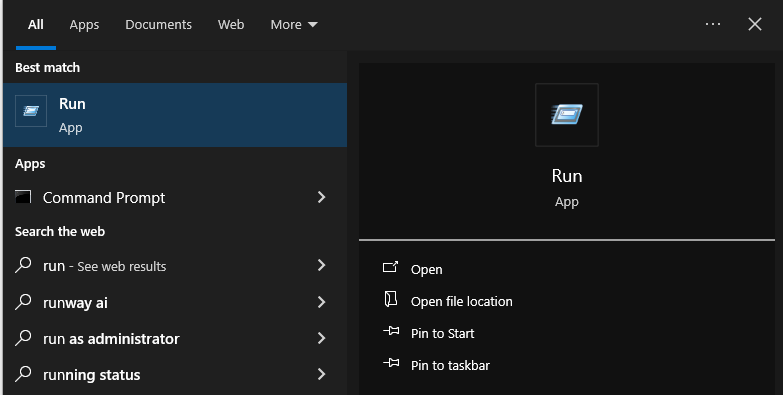
- Type “inetcpl.cpl” and press OK.
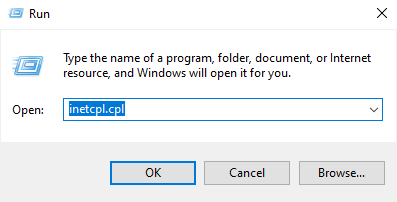
- In Internet Properties, go to the Advanced Tab and click Reset.
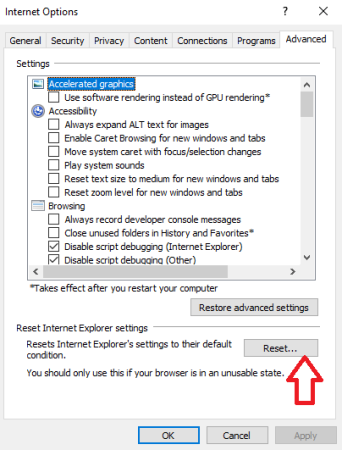
- Check “Delete Personal Settings” and click Reset.
- Wait for IE to finish and click Close.

This process refreshes IE, clearing settings and personal data.
Method 4. Reset IE by deleting user profiles
Resetting Internet Explorer using the registry is a bit tricky, so be careful and back up your registry first. Here’s how:
- Open the “Registry Editor” by typing “Run” in the search bar and clicking on it.

- Type “regedit” and press Enter.
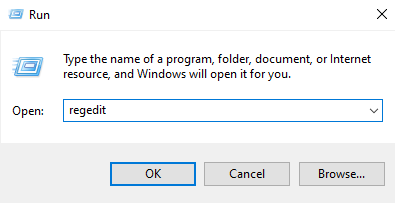
- When asked by User Account Control, click “Yes” to allow changes.
- In the Registry Editor, find and delete a key called “[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\Microsoft\\Internet Explorer].” Confirm by clicking “Yes” to delete it and everything under it.

- Next, delete anything related to IE under “Application Data” or “Local Settings.”
This process clears out IE’s settings, but be cautious because mistakes here can cause problems. Backup your registry before you start in case you need to undo any changes.
Method 5. Reinstall Internet Explorer
If none of the previous methods worked to fix Internet Explorer (IE), you can try reinstalling it. Here’s how:
Uninstalling IE:
- Go to the Control Panel and look for “Uninstall a Program” (or “Add/Remove Programs” in older versions of Windows) under the Programs section.
- Click on “Turn Windows features on or off.”
- Find “Internet Explorer” in the Windows Features window, uncheck it.

- Confirm by clicking “Yes” and then “OK.” This may require a computer restart.
Reinstalling IE:
Now, you have two options to reinstall IE:
Option 1:
- Go to the Control Panel, then “Uninstall a Program” (or “Add/Remove Programs”).
- Click “Turn Windows features on or off.”

- Check “Internet Explorer” in the list, click OK, and wait for changes to apply. Restart your PC if asked.

Option 2:
Use another web browser already installed on your computer and visit the official Internet Explorer website to download and install it.
This process ensures you have a fresh installation of IE on your computer. If IE was causing problems before, this might help. But remember, you can also consider using other more modern and secure web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, or Edge as alternatives to Internet Explorer.
Remove browser hijacker from Safari

Safari used to be a really secure web browser for Macs, but things changed in 2015. Now, it’s the second most popular browser, and lots of bad actors like advertisers and scammers are targeting it to make money.
Some of these bad programs can change Safari’s start page and search engine to send you to websites they want you to visit. But don’t worry, you can get rid of these annoying things easily.
First, it’s a good idea to run an antivirus scan on your computer to make sure there aren’t any hidden problems. This will help get rid of anything bad that might have brought these issues to your Mac.
Then, you can reset Safari’s settings. This means taking it back to its default state, like when you first installed it. It’s like giving your browser a fresh start.
This should help you get rid of any annoying stuff that’s been added to Safari and keep your web browsing safe and clean.
Before resetting Safari, make a backup of important data. Then, follow the steps in this guide to reset Safari and clear unwanted changes while keeping your vital information safe.
Method 1. Erase browsing history in Safari browser
Resetting Safari by clearing its history is easy. Just follow these steps:
- Open Safari.
- Click on the “Safari” menu at the top.
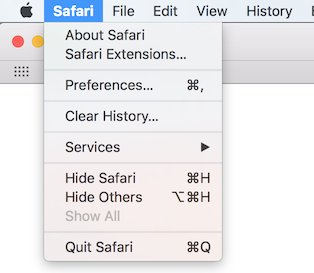
- In the menu, select “Clear History…”
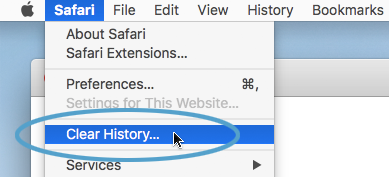
- You can pick how far back you want to erase your browsing history, like the last hour or all of it.
- Click “Clear History.”

This will remove the websites you’ve visited and any saved data. It’s a quick way to clean up your browsing history in Safari.
Method 2: Clear out web caches in Safari browser
To fully reset Safari, you might need to clear its web caches, especially if the first method didn’t fix your browser problems. This can be a bit trickier to find because it’s in the “Develop” menu.
Here’s how to do it:
- Open Safari.
- Click on the “Safari” menu and pick “Preferences…”
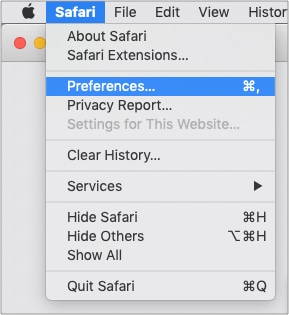
- In the window that opens, go to the “Advanced” tab.
- Check the box that says “Show Develop in the menu bar.”

- You’ll see a new “Develop” option in the top toolbar.
- Click on “Develop” and choose “Empty Caches.”
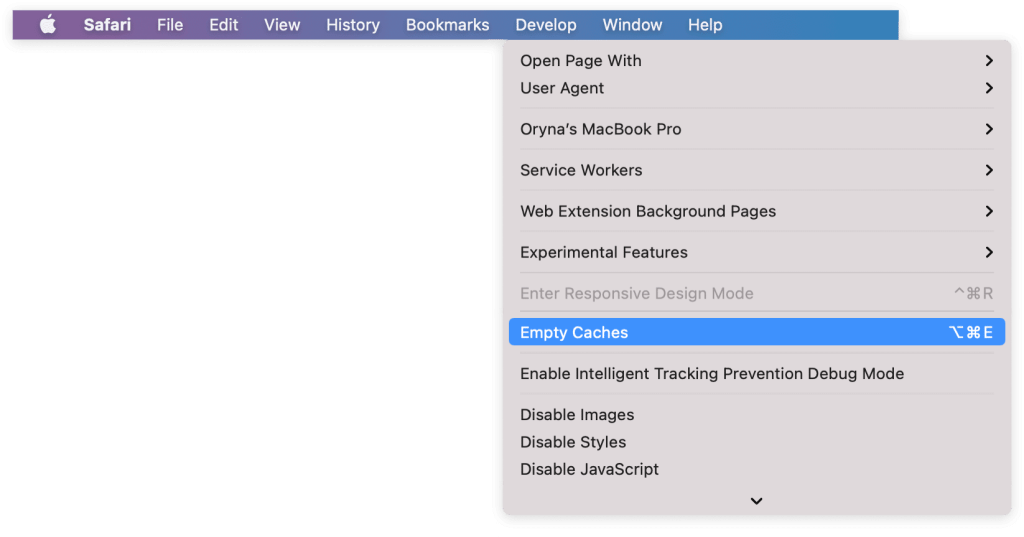
If you want a faster way, you can press “Option + Command + E” at the same time.
This helps clear out stored data that might be causing issues in Safari.
Method 3: Remove harmful or suspicious extensions from Safari
Sometimes, when you add new stuff to your web browser like extensions or plugins, it can make your browser act strangely. This can happen because some extensions, which are supposed to make your browsing better, might be created by shady developers who want to do bad things like collecting your information or sending you to unsafe websites.
If the previous methods we talked about didn’t fix your browser issues, you should check if there are any bad extensions causing the problems. Here’s how you can do it:
- Open Safari.
- Click on the “Safari” menu and choose “Preferences…”
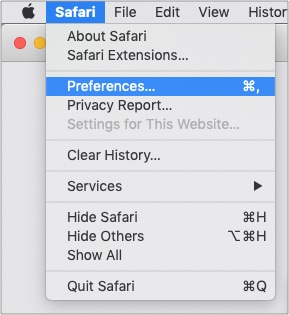
- In the window that pops up, click on the “Extensions” tab.

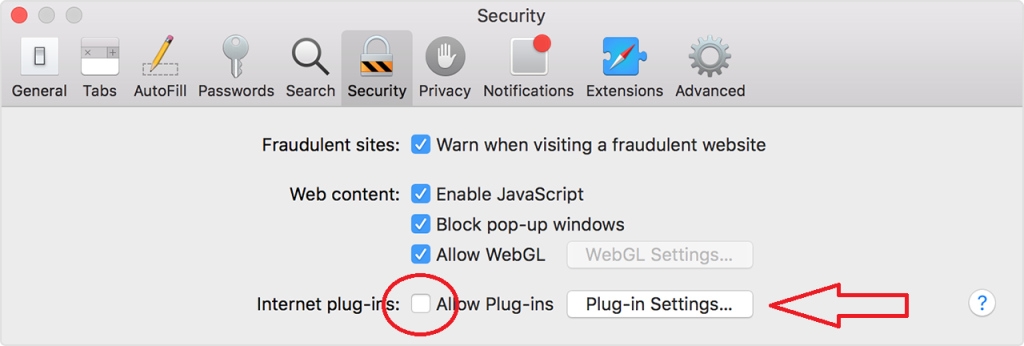
- Look at the list of extensions carefully. If you see any that you didn’t add or look suspicious, remove or disable them. You can even turn off all extensions to see if that’s what’s causing the trouble.

- After dealing with extensions, go to the “Security” tab and uncheck the box that says “Allow Plug-ins.” You can also customize which websites can use plugins by selecting “Plug-in Settings…”
- Finally, restart Safari after doing all these steps.
This should help you get rid of any bad stuff that’s causing problems in your browser and make it work better.
Method 4. Manually restore Safari to defaults
Sometimes, the usual methods for resetting Safari might not completely fix the problems you’re facing. In such cases, you can try a deeper reset by moving some important folders and deleting certain files. Here’s how to do it:
- Close all open programs.
- Click on the “Go” menu in the top toolbar.
- While holding down the “Option” key, you’ll see a new option called “Library” – click on it.
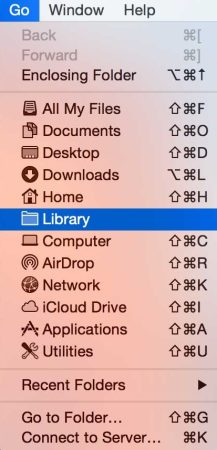
- In the Library window, find the “Safari” folder and move it to your desktop or somewhere safe.
Next, go back to the Library folder and delete specific files from these folders:
- In the “Saved Application State” folder, look for a folder named “com.apple.Safari.savedState” and delete it.
- In the “Caches” folder, find all folders that start with “com.apple.Safari” and delete them.
- In the “Cookies” folder, find a file called “com.apple.Safari.SafeBrowsing.binarycookies” and send it to the trash.
- In the “Preferences” folder, delete any files that have “com.apple.Safari” in their names.
By combining these manual steps with the built-in features we talked about earlier, you should be able to fix issues with your Safari browser and enjoy smooth browsing once again. This deeper reset helps you get rid of any stubborn problems that the regular reset might not solve.
Using Anti-virus or Anti-malware Tool (A User Friendly Browser-Hijacker Removal Process)
Free antivirus software is like a guardian for your computer. It’s essential because you can’t always tell if a website or download is safe. These programs help by stopping viruses and malware from sneaking into your device. They work like a security wall.
One cool thing about them is that they can check for browser hijackers in real-time. Imagine someone trying to take over your browser and redirect you to bad websites. Antivirus software spots this and stops it before it even gets to your browser. It’s like a bodyguard for your web surfing.
Also, they have tools that watch out for identity theft. This means they keep an eye on your personal information to make sure no one is stealing it online. It’s like having a detective who protects your private stuff.
So, having free antivirus software is like having a strong shield for your computer. It keeps the bad stuff out and keeps your personal info safe, so you can surf the web with peace of mind.
Comparing Security Software Options

Numerous anti-malware tools are available, each designed to detect and remove malicious software from computers and devices. These tools vary in features, effectiveness, and user-friendliness. Popular options include Malwarebytes, Bitdefender, Norton, and McAfee. Users should choose one that suits their needs and regularly update and scan their systems for optimal protection.
Malwarebytes: Malwarebytes used to be a special tool for fixing computer problems, but now they have Malwarebytes Premium, which is like a regular antivirus. It can scan your computer when you want, and it watches for bad stuff happening in real-time. If it sees something fishy, it stops it. It’s good at finding things like ransomware and sneaky attacks. So, it’s not just for fixing issues; it’s an all-around protector for your device, like a strong guard that keeps an eye on everything to make sure it’s safe.
Bitdefender: Bitdefender Antivirus Plus is more than just an antivirus; it’s like a superguard for your computer. It protects you from viruses, but it also does a lot more. It keeps your online banking safe, shields you from sneaky ransomware, hides your identity with a VPN, stops annoying ad trackers, and even helps you manage your passwords. It’s like having a superhero program that keeps your device safe from all sorts of threats and makes your online life easier and more secure.
Norton: Norton AntiVirus Plus is like a super-strong guardian for your computer. It’s not just antivirus; it also has a firewall that protects your device from attacks outside and even from sneaky threats within. It won’t bother you with confusing pop-up questions. It can also find and stop tricky attacks. It offers a backup system for your files, a spam filter, a tool to keep your software up to date, and more. It’s like having a powerful shield that keeps your computer safe from all sorts of dangers, both inside and outside, and offers extra tools to make your digital life easier and secure.
McAfee: McAfee AntiVirus Plus is like a protective shield for your main computer, and the cool part is, with just one subscription, you can use it on all your other devices like laptops, phones, and tablets. This means every device in your home gets the same level of protection. When all your devices are safe from threats, it helps keep your entire network secure, like having a strong defense team for your digital world.
Prevention from Browser-Hijacker in Future

To protect your browser from being hijacked, follow these steps:
- Keep Your System and Browser Updated: Make sure your computer’s operating system and web browser are up to date. Updates often include security improvements that can prevent hijacking attacks.
- Be Cautious with Software Downloads: When downloading new software, carefully read the terms and conditions and user agreements. Some browser hijackers come bundled with legitimate software, so be cautious about what you install.
- Watch Out for Freeware: Be careful with freeware programs that may try to install additional software during installation. Always check the download settings and unselect any unwanted extras.
- Avoid Suspicious Links: Don’t click on links in emails, messages, or pop-up windows from unknown sources. Clicking on these links can lead to the download of browser hijacking software.
- Use Antivirus Software: Install reliable antivirus software and keep it updated. Antivirus programs can protect against browser hijacking in real time by warning you when downloaded software attempts to change browser settings. Some even let you stop these changes from happening.
By following these steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of your browser being hijacked and ensure a safer online experience.
In conclusion, browser hijacking is a malicious practice where unauthorized changes are made to a web browser’s settings, often leading to unwanted redirects, altered homepages, and privacy breaches. Users can protect themselves by keeping their operating systems and browsers updated, exercising caution when downloading software, avoiding freeware with hidden installations, refraining from clicking on suspicious links, and using antivirus software for real-time protection. Being vigilant and proactive is key to preventing browser hijacking and maintaining a secure online environment, safeguarding personal information, and ensuring a smoother browsing experience.